"From Vice Presidents to Wall Street Titans" — The 'Rockbridge Network' Tightens Grip on U.S. Politics
Input
Changed
Rockbridge Network Emerges as Power Center of Trump’s Second-Term Administration Founder JD Vance, Now U.S. Vice President, Eyes 2028 Presidential Run Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent Tipped as Potential Next Fed Chair

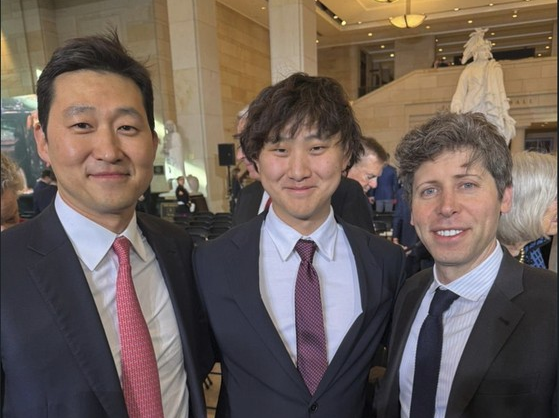
The powerful new conservative force in the United States, known as the Rockbridge Network, is tightening its grip on American politics. A complex web of key figures from the Trump administration and investment heavyweights is exerting massive influence across American society. At the center of it all is JD Vance, the U.S. Vice President and founder of Rockbridge, who is reportedly aggressively positioning himself for a presidential bid in the next election.
Rockbridge Played a Key Role in Trump’s Re-election
According to sources in both U.S. and Korean political circles, the political fundraising group Rockbridge is emerging as a central force of power in Washington. Founded in 2019 by Vice President Vance and conservative columnist Christopher Buskirk, Rockbridge aimed to build a political base for a new conservatism to replace the fading traditional Republican establishment.
Membership is exclusive—USD 25,000 grants access to events, while lifetime membership costs USD 1 million. The group spends approximately USD 75 million annually on political activities, including candidate support, shaping public opinion, and voter outreach.
Rockbridge made its name during last year’s U.S. presidential election. In April, Trump’s campaign was cash-strapped and facing a cornered position in the GOP primaries, as traditional donors like the Koch network supported Ron DeSantis and Nikki Haley. That’s when Rockbridge stepped in, injecting large sums of money into Trump’s campaign and recommending Vance as the running mate. Donald Trump Jr., a Rockbridge member, brokered the connection.
Notable Influence of Rockbridge Members
Rockbridge’s ability to exert such influence stems from the heavyweight names within its ranks. At the center is Peter Thiel, founder of Palantir and longtime mentor to Vance, often described as the network’s “puppet master.” Elon Musk, Tesla CEO and head of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) in Trump’s second term, is also a member. Other prominent figures include the Winklevoss twins, who donated USD 1 million worth of Bitcoin to Trump; hedge fund titan Rebekah Mercer; White House Chief of Staff Susie Wiles; Secretary of State Marco Rubio; Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent; Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr.; and Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard—all current members of Rockbridge and influential figures in the administration.
These figures are leaving their mark across the U.S. political landscape. Trump Jr., although holding no official title in the second Trump administration, has been instrumental behind the scenes, assisting with appointments and lobbying globally to expand Rockbridge’s reach.
Vice President Vance is rapidly solidifying his power. He made headlines in March when he interrupted a meeting between Presidents Trump and Volodymyr Zelenskyy of Ukraine, telling Zelenskyy to “thank America” in a stern tone. The moment symbolized a shift from America’s global policing role to an “America First” stance.
Vance’s ambition clearly points toward the next presidential election. Many believe he intends to inherit Trump’s political mantle and carry forward the “Trumpism” agenda. One foreign policy expert commented, “Rockbridge is a powerful alliance of America’s new economic elite and political power—and Vance stands at its center. If their plans come to fruition, Vance will become the standard-bearer of America’s new conservatism.”

Treasury Secretary Bessent Tipped for Fed Chair
Scott Bessent, Rockbridge member and Treasury Secretary, is a strong contender for the next Chair of the Federal Reserve. According to a June 10 report by Bloomberg, Trump’s advisors are backing Bessent for the role. The Fed Chair is nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate, with a four-year term. Jerome Powell’s term ends in May next year.
Bessent, a respected figure on Wall Street, is spearheading key initiatives in the Trump administration, including U.S.–China trade negotiations and tariff policies. His expanded role has reportedly won Trump’s deep trust. Even in a power struggle with Elon Musk over the acting IRS commissioner position, Trump sided with Bessent.
Steve Bannon, former Trump strategist, praised Bessent, saying, “He proved during the volatile early months of Trump’s presidency that he could deliver on the promises. He’s not just competent—he’s someone global markets can trust.” Tim Adams, President of the Institute of International Finance (IIF), added, “Given the global financial community’s trust in him, Bessent is undoubtedly a strong dark horse candidate.”
Other potential Fed Chair candidates include former Fed Governor Kevin Warsh, whom Trump recently praised as “highly regarded.” However, Arthur Laffer, former University of Chicago professor and close Trump advisor, commented, “Bessent is excellent, but already has a major role and isn’t primarily a monetary policy expert. I told the President Kevin Warsh would be perfect for this position.” Additional names being floated include Kevin Hassett (former Chair of the White House Council of Economic Advisers), Fed Governor Christopher Waller, and former World Bank President David Malpass.